Authentication
iSHARE uses the OAuth 2.0 protocol for authenticating parties and providing access tokens based on the iSHARE agreements when requesting access to a service within iSHARE. For the most recent version of the OAuth 2.0 specification visit oauth.net. In addition to the OAuth 2.0 specifications, the following requirements apply for iSHARE:
Clients MUST NOT be pre registered. A look-up in the iSHARE adherence registry is sufficient. It is up to the server create a new entry for Clients that perform requests for the first time.
The client_id MUST contain the valid iSHARE identifier of the client.
In case of potential HTTP message size restrictions on the server, a POST call alternative MUST be offered to the /oauth2.0/token endpoint. Therefore, to avoid unaccepted HTTP GET calls, HTTP GET calls MUST be disabled to the /oauth2.0/token endpoint.
Servers MUST NOT issue refresh tokens
In OAuth 2.0 clients are generally pre-registered. Since in iSHARE servers interact with clients that have been previously unknown this is not a workable requirement. Therefore iSHARE implements a generic client identification and authentication scheme, based on iSHARE whitelisted PKIs.
Note
M2M Interaction sections explain how authentication and authorization happens within iSHARE. Authentication part requires a proper /token endpoint implementation. If you are already familiar how authentication works within iSHARE and ready to implement the endpoint, please visit access token section.
Generic Authentication Flow
Based on the described standards and specifications in this scheme, the generic iSHARE Authentication flow is described in the following sequence diagram.
For a deeper understanding of the various roles within the iSHARE Trust network, take a look at the framework and roles page in the official iSHARE Scheme of agreements.
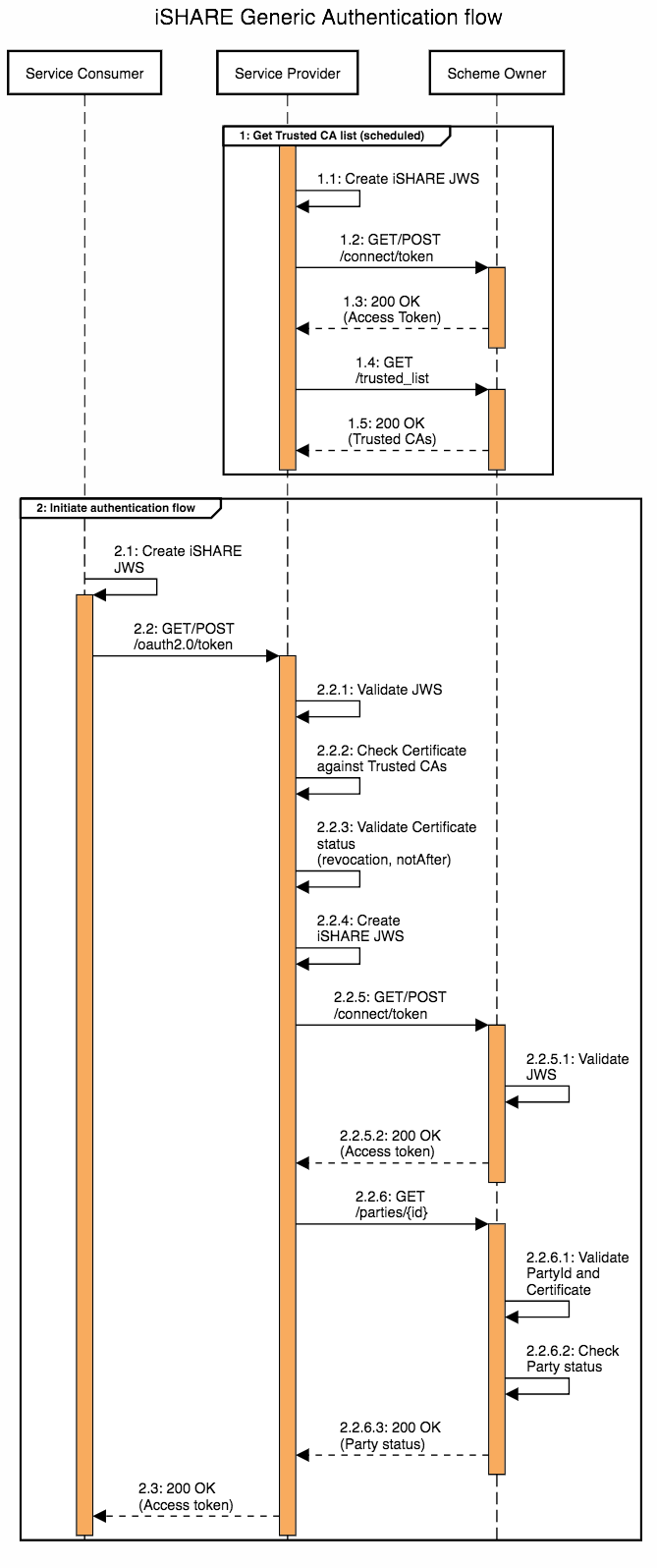
The sequence diagram refers to Service Consumer, Service Provider and Scheme Owner. Please note that this Authentication flow applies to various possible interactions. Each party that needs to authenticate another party requesting data or services can be authenticated through this flow.
In the demo section you can find Postman Collections that demo this authentication flow from the perspective of a Service Provider.
In this flow chart, we describe the steps within the authentication flow in greater detail.
Certificate Validation
Validating the certicate mainly consists of two steps:
Verifying the validity of the certificate (steps 2.2.2 and 2.2.3 of the above generic authentication flow).
Verifying the iSHARE Status of the party (step 2.2.6 of the above generic authentication flow).
It is always the responsibility of the receiving iSHARE Party to verify the certificate and the status of the requesting iSHARE Party! During conformance testing (see Conformance Test Tool) we can only test how you validate test-certificates. It is important to make sure that real certificates are validated in a proper way, as described below.
1. Verifying the validity of the certificate
A request in iSHARE must always be signed by a certificate that is issued by a certificate authority on the trusted list of iSHARE. Participants can get the trusted list via the /trusted_list endpoint. The trusted list consists of PKIoverheid certificate authorities and qualified Trust Service Providers under eIDAS. The party receiving the request signed by such a certificate is responsible for verifying that the certificate is issued and signed by a certificate authority on the trusted list.
2. Verifying the iSHARE Status
Within iSHARE, it is necessary to match the identity on the certificate that is used to sign the client_assertion with the party identifier (EORI) within that client_assertion. It is possible that the EORI is not recorded on the certificate. Therefore, the standard procedure to verify the status of an iSHARE Party is as follows:
Substract the certificate’s full subject_name from the x5c-value.
Send a request to the /parties endpoint of the Scheme Owner. Parameter
eorivalue should beclient_idfrom request (it should be equal toissorsubinclient_assertion). Parametercertificate_subject_namevalue should be the extractedsubject_namefrom the x5c-value, every certificate attribute that exists insubject_nameshould be also present incertificate_subject_name, if at least one attribute is missing validation fails.Decode the parties_token received and check the signature.
In the information, the status of the party is listed under “status” and should be equal to “Active”.
Example of iSHARE status verification of ABC Trucking:
The
x5cvalue of ABC Trucking’s request:
MIIEgTCCAmmgAwIBAgIIN9ViCDi3BwswDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAwSDEZMBcGA1UEAwwQaVNIQVJFVGVzdENBX1RMUzENMAsGA1UECwwEVGVzdDEPMA0GA1UECgwGaVNIQVJFMQswCQYDVQQGEwJOTDAeFw0xOTAyMTUxMTQ2MTVaFw0yMTAyMTQxMTQ2MTVaMEIxFTATBgNVBAMMDEFCQyBUcnVja2luZzEcMBoGA1UEBRMTRVUuRU9SSS5OTDAwMDAwMDAwMTELMAkGA1UEBhMCTkwwggEiMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4IBDwAwggEKAoIBAQC0O4hUhD+VoOKVIZSNMNTfzc0O2kYj+ZzpQEABZGtPty0kKPJep0+o5xstou1K+UxvHfxEpHxHGTdtqZuc28LhU4CeCgoeDMDT+CHS3NosiESQMwh/ZZeTc9/eKCo569GCn+2XtTiGSpBSwMSWqNHgpAZYKdHrT/kEMIyTKoauuiKQ8cUp7ow7mZz/9K+qV3s9L030W8IawLJBJK/2apAt5jh1j4/mF7f0q8zhzhrC8v01PLlZduTzjjBre7mz+yi/vlYz/eap0eYTjhxIatyV9FFwlmi4FC1CNcMtLh8nsiJoe5cBm13LKbQFu3GYH76oeLZvWqbPbp11mxlHa/KdAgMBAAGjdTBzMAwGA1UdEwEB/wQCMAAwHwYDVR0jBBgwFoAUFjznIOnWlO8f5aLxuPy+6t8sN4EwEwYDVR0lBAwwCgYIKwYBBQUHAwEwHQYDVR0OBBYEFAPH+8UrYiVLXaKPRGflkA+cusQ7MA4GA1UdDwEB/wQEAwIFoDANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAgEAYl5tWH0YtYS9JyqylZJWomA55ShKllaBRcvro6CHxllJWHo0qC9ZTMcvCywMv14VJyQd6eFZqcVtOluGrRZBklH9Aankovp2JLaqcD79t1CyuXZnIzTFl/BkMsE6wlAJXY/sarnoxeiejP4E/Ef/0euIFvBaICCF+Kd2WJYbbn0Wy0dH484QJbHyMtVfr42oIpUNVuLSu84yKYAem9JBuYTp3Y0K2hiEAW/bOKDvvHetVf5fu66yfekDX53j3NKiFJCXS2rKIZoDuMFuxpSyVkS2kbWk1+5Joy7qOSNANRFPlpHcgzLQZp8HrgvhsmhIt1VTVYkyxcd8qXAlhwqVgOq5NgLxkqul9hNMGiM7sq+H73Q/Fi8if7gP8IVASzQGwuHg2Z87ib6A2von0fRJZq3fIubHoxI63ATwfcRK86y172xbFE3VU0duN1tI5Z0TCg0GAJYtJpbnvexIt5lk5FIk4ThvR0L8mNLy1DUa11N+EMxkqbfqlTurB8Zg3CY/QaSKmXY5CMUwWeEBXRHhyfkZQ5jPPUHrFaoyORX8p1ErYDktB1K9o4jmuEVpB33cvgYBEiAyV5z4426FuVCMbHaFDV7iKW9eBlXoxeZo4XX8+jXySL5GW8XwNRTK5c4vW02Q3VJyYVe5umestsKQ+LR8iAzoUSreK18+JkAjAJU=
The extracted
subject_name:
C=NL, SERIALNUMBER=EU.EORI.NL000000001, CN=ABC Trucking
The call to
/partiesendpoint to verify the iSHARE status:
GET /parties?
eori=EU.EORI.NL000000001&
certificate_subject_name=C=NL, SERIALNUMBER=EU.EORI.NL000000001, CN=ABC Trucking
(URL encoding removed, and line breaks added for readability)
The decoded response lists ABC Trucking as “Active”:
{
"party_id": "EU.EORI.NL000000001",
"party_name": "ABC Trucking",
"adherence": {
"status": "Active",
"start_date": "2018-04-26T14:59:03",
"end_date": "2019-07-25T14:59:03"
},
"certifications": [],
"capability_url": null,
}